Linux Mint is one of the most popular (GNU/
Linux)
operating systems around, and according to
Distrowatch.com‘s
popularity ranking factor, for many years now Linux Mint has been on
the top 3 most popular distributions (now it’s actually the number one!,
surpassing Debian and Ubuntu. By the way, Fedora’s ranking is sinking
fast, no surprise there though. Fedora is just a distribution for the
coding elite of the GNU/Linux world and not for the average user, there I
said it!). And there’s a good and a sensible reason for it (in my
opinion anyway).
The reason is, with Linux Mint there is a sense of continuity where
by change, it progresses. In other words, compared to the ‘radical’ and
often chaotic changes that some other desktop environments bring such as
GNOME, ‘change’ in Linux Mint is progressive. For instance, if you look
at the evolution of the Cinnamon desktop (first released in 2011), so
far it has been very consistent (UI-wise), yet, things have been vastly
improved and hundreds of new features added. But if you look at the
evolution of GNOME, by each major release (1x -> 2x and then from 2x
-> 3x) there has been radical changes through which an entirely
different looking (and functioning) desktop emerged. And sometimes the
end result is quite chaotic for many end-users.
That being said, “Are radical changes bad?” That I cannot say.
However, it’s usually the young and the energetic who are more prone to
make radical choices. The old, the experienced and the settled, usually
is more careful in their choices because experiences have taught them
that
there is a guaranteed positivity in change when it’s progressive. The best example is to
look at the evolution of the Apple Mac OS.
I mean look at the below screenshot. That’s how Mac OS used to look in
1984! And here we are after 32 years where so many radical changes have
occurred, yet amazingly, the core identity of the desktop is still
there, is it not?

I don’t know what the future will bring for Linux Mint’s Cinnamon
desktop environment, but here I am using the latest version of it (Linux
Mint 18, Cinnamon) after 2 years, and for the past 3 days, I
experienced the same stability, fastness, efficiency and although vastly
improved, the same looking desktop environment that was there, not only
2 years ago, actually it was like this from the very beginning.
And the users don’t complain!
And according to Linux Mint developers, it’s actually the 3rd most
popular operating system used on Earth, after Microsoft Windows and Mac
OS. That’s how it should be done, methinks. And speaking from a software
developer’s point of view, I think it’s alright to make radical changes
at the early stages where one is still in the process of creating a
core identity. But once you’re past it, you should move on with
progressive steps not chaotic confusions. For instance, Ubuntu came up
with Unity and it was a radical change back then, a totally revamped
desktop UI. And they should better stick with it for many years to come.
Otherwise, if all you ever do is introducing chaotic changes on how
things are done,
you either are a genius or an idiot who don’t have a clear goal in mind, let alone displaying the lack of instinctively mastered skill.
The philosophical lesson is over, let’s move on with the Linux Mint 18 Cinnamon Review
. So as soon as I heard a new version of Linux Mint has been released I
downloaded the Cinnamon edition right away. Linux Mint is not
restricted to their in house built Cinnamon desktop but also
features the Xfce (not updated to the ’18’ release yet) and the
MATE desktop. But I always was very interested in Cinnamon (I mean the
desktop, yes, love the vegetable also ) and that’s all I’ve ever used with Linux Mint so I decided to use it here for the review also.

The Cinnamon flavor comes with Cinnamon desktop 3.0.6, Kernel 4.4,
X.org 1.18.3 and is based on the Ubuntu 16.04 LTS core. The disc image
size is about 1.7 GB. Linux Mint

Cinnamon 18 will be supported up to 2021 with security fixes. UEFI is fully supported, but you need to turn off ‘Secure Boot’,
otherwise you’re required to do some work.
I don’t have performance related data from a recent Linux Mint
Cinnamon release, thus I decided to compare its performance with Ubuntu
16.04 LTS. However, when I was done
reviewing Ubuntu 16.04 LTS and
Ubuntu 16.04 Flavors comparison,
I received a new laptop. So I decided to install Ubuntu 16.04 LTS on it
before I installed LM 18 Cinnamon on the new laptop. Then I re-measured
the performance related data because comparing two distributions that
were used on two totally different hardware doesn’t make any sense. And
as always, before I begin the Linux Mint 18 Cinnamon review, here’s
brief description of the hardware details of the new laptop:
Intel Core i7-5500U, Hybrid GPU Setup (Intel Broadwell HD
Graphics 5500, Nvidia 920M), 4GB RAM DDR3, Hybrid Permanent Storage
Setup (Seagate 5400 RPM, 500 GB rotational disk and a Kingston 24 GB
SSD), Qualcomm Atheros AR9565 Wireless Adapter, Realtek
RTL8111/8168/8411 PCI Express Gigabit Ethernet Controller, Realtek
ALC3236 Sound Card, LED Display (1366 x 768 resolution, 60 FPS/HZ). It's
an Asus laptop (F302LJ-FN024H).
This laptop as you can see, includes two storage devices. One 500 GB
rotational disk and another 24 GB SSD, both separate drives (not a
2-in-one type hybrid drive where a single controller controls both the
SSD and the rotational disk). And since I don’t have a lot of SSD space
remaining, and since I’ve installed the main operating system on the 24
GB SSD (I use it as the ‘root’ partition actually, the ‘Home’ partition
is located on the rotational disk), I installed Linux Mint 18 Cinnamon
into the conventional and the slower, rotational HDD instead.
As always, also remember that, after installing the OS, I boot(ed)
into the OS 5-6 times for letting things to settle down (first time
‘wizards’ and background system services to be done with their setups)
and then I disabled the Startup Welcome screen and the Update manager
from running to keep the accuracy of the memory usage readings high.
User auto-login was also enabled and I also added System Monitor
shortcut to the task-bar. And only after measuring the performance
related data (boot-up times, memory usage, power usage, system
responsiveness, shutdown delay) I started to use the operating system
and discover what’s new.
Also kindly remember that I’m using Linux Mint Cinnamon with a 2 year
absence. Therefore, some of what I may say ‘new’ might already have had
been there in the past.
The Installer, GRUB & Boot-Up Logo…
I’ve decided to skip both the installer, the boot-up logo & GRUB.
First of all, LM 18 uses Ubuntu 16.04 LTS installer and I’m sure you
all are familiar with it. Secondly, the GRUB and boot-up logo haven’t
changed either. Therefore, I’ll go over to the Desktop straightaway.
The Desktop

Except for the new wallpaper, it’s a typical Cinnamon desktop UI
where a Microsoft Window’s traditional looking desktop is presented (a
task-bar at the bottom of the screen with a ‘XP’ type start-menu. Come
on now, you know all these details
). The desktop right-click context menu has changed a bit though. It’s
filled with couple of useful shortcuts, ‘Desktop Settings’ is a newly
added shortcut if I’m not mistaken.

If you find it consists of too many shortcuts, then you can easily
disable a few through the file manager -- Nemo. This is because some
elements of the desktop (desktop icons and the right-click context menu)
is controlled through the file manager. For that open the file manager
and go to ‘
Edit‘ -> ‘
Plugins‘, then under ‘
Actions‘ you can disable some of the items from being displayed on the desktop context menu.

Nemo (a fork of GNOME’s file manager) also contains many useful
features unlike the GNOME file manager. For instance, nowadays GNOME’s
file manager doesn’t have a ‘Compact View’ option which I used to like
quite a lot when viewing folders filled with files and other folders as
it saves display space. Nemo however, still has it. Through the ‘
Preferences‘ -> ‘
Toolbar‘
section, you can also add/remove a few more features (‘open terminal’,
‘create new folder’ etc) into the main toolbar as well. And unlike the
GNOME’s file manager, Nemo allows more customization options too.

One annoying issue I found while using the Cinnamon desktop is the
‘Window list Thumbnails’. Cinnamon displays a thumbnail of docked
applications on the bottom task-bar when you move the mouse pointer over
them. But the problem is, as long as you keep the mouse pointer over
it, it never fades away! For instance, let’s say that I was using the
text editor and moved mouse pointer over the terminal window on

the
task-bar to see a preview (let’s say I was running a command and wanted
to see if it has been finished. Yes the thumbnails update in
real-time). Then after looking at the thumbnail update, if I started to
re-type on the text editor window without taking the mouse pointer away
from the docked terminal window, the thumbnail stays there forever
overlapping with the text editor. A major distraction. The only solution
is to completely disable the thumbnails, but I quite like them. So one
suggestion I would like to make to the Linux Mint developers is
how about stop showing the thumbnails as soon as a user starts to use his/her keyboard,
even if the mouse pointer is focused on a certain application window
docked on the task-bar? That’s a better approach because if the keyboard
starts receiving inputs, it means then the user focus is in somewhere
else.
One of the other major changes of the Cinnamon 3.x desktop is that
there is now a brand new theme called ‘Mint-Y’, although by default, the
old ‘Mint-X’ is still used. From new icons to colors (icons, menu items
etc) and to how the buttons look like on application windows, ‘Mint-Y’
brings major changes. It’s looks flat but still retains a subtle 3D
look, a very modern looking theme. I like it a lot. The reason it isn’t
applied by default is because it’s still in active development if I’m
not mistaken.



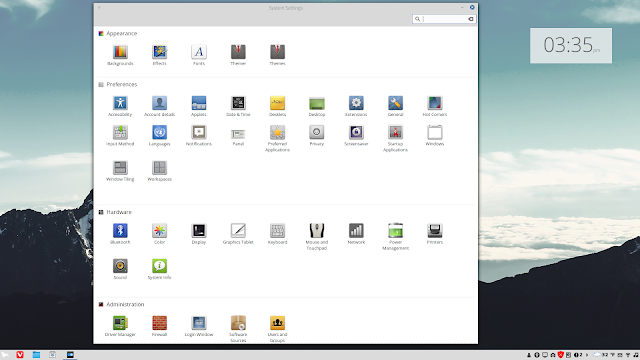
The ‘System Settings’ has always been quite impressive with Linux
Mint as it gave access to so many customization options without
compromising simplicity. This release is no exception, except, compared
to my Linux Mint 17, now there are many more options, and under each
settings window (‘Applets’, ‘Desktop Settings’, ‘Windows’, ‘Power
Management’, ‘Notifications’ etc) options are categorized &
listed under tabbed windows. This again has helped Linux Mint to retain
its simplistic approach, yet still to present lots of customization
options to the user.

The Update Manager also has received a new option to easily set its
behavior. By simply choosing between 3 available options, users can make
Linux Mint Update Manager to:
- Update the system with stable versions of software
- Update the system with stable versions of software as above, but
show whether the user would like to install additional updates which
could lead to instability issues
- Update everything, and if something breaks, then you better had known how to fix it!

I quite liked this feature. The settings page alone looks very professional.
Introducing X-Apps
This is the other major change in Linux Mint 18, it’s called ‘X-Apps’.
According to Linux Mint’s founder Clement, the reason for their existence is as follows:
Work started on Linux Mint 18. One important aspect is
GNOME 3.18 (the project and all its components, not just the desktop
environment), which includes GTK and many applications used primarily by
Cinnamon, but also Xfce and to a lesser extent MATE. A lot has changed between version 3.10 (used in Linux Mint 17) and version 3.18. GTK itself and many
of the GNOME applications now integrate better with GNOME Shell and
look more native in that environment. The bad news, is that they now
look completely out of place everywhere else….
… From a long term point of view, we knew this would become more and
more of an issue but it was decided early that Cinnamon would not get
its own applications, because it represented too much work and there
were too few differences in application needs between Cinnamon, MATE and
Xfce. It just made no sense to invest time in making “Cinnamon
applications”. For similar reasons we invested very little time in
developing MATE applications.
The idea of working on apps which would be generic, perfectly suited to run in both Cinnamon, MATE and Xfce
(and possibly other desktop environments) made more sense. It’s an idea
we’ve had for a while and with the start of a new Mint 18.x series the
timing was right to get this project started.
Basically, X-Apps are a collection of existing GNOME (3.18)
applications that are redesigned (patched) to work across three main
flavors of Linux Mint: Cinnamon, MATE and Xfce. In other words, rather
than developing these applications for each flavor individually
(which’ll take a lot of human effort & time) they’ve centralized the
development in such a way so that they can develop each application to
work across all 3 flavors simultaneously.
Currently Linux Mint 18 Cinnamon edition ships with 4 X-Apps: xed
(text editor), Xreader (document viewer), Xviewer (image viewer),
Xplayer (video player). Again, they’re all existing GNOME applications
but patched to work (mainly being displayed correctly without themes
related issues etc) across all 3 flavors of Linux Mint.
Some Of the Applications Included:
Linux Mint 18 Cinnamon ships with updated software tools such as:
Firefox 47.0, Thunderbird 38.7.2, GIMP 2.8.16, LibreOffice 5.1.2.2, Pix
1.0.5 (image organizer), Transmission 2.84, Banshee 2.6.3, mintinstall
Software Manager 7.7.3, synaptic software manager 0.83. These are just a
few to mention.
P.S: Unlike in Ubuntu 16.04 LTS where it struggled
to install ‘.deb’ files by default, in Linux Mint 18 they can be
installed without any issues because the ‘.deb’ files are handled by a
separate utility (gdebi -- Ubuntu doesn’t include it by default).
 Multimedia Playback, Adobe Flash and Skype
Multimedia Playback, Adobe Flash and Skype
Linux Mint 18 Cinnamon doesn’t ship with
proprietary multimedia codecs
by default, although it used to include them in the past. However,
there is a dedicated software (GUI) that can be used to install all the
necessary proprietary multimedia codecs easily. Just type in ‘codecs’
into the start-menu and you’ll find it.
Linux Mint 18 also includes a command-line tool for creating an offline-
multimedia
codec pack too! You can use this command-line utility on a Linux Mint
18 live DVD/USB drive on a computer that has internet access to create a
codec pack, and then use that to install those codecs on a computer
that’s running Linux Mint 18 that doesn’t have an internet connection.
To do that, once boot(ed) using the live media, open the terminal and
enter the below command:
apt download mint-meta-codecs

This will create a compressed file called ‘mint-meta-codecs.tgz’ on
the Home folder of the live DVD/USB. And on a computer where you have
installed Linux Mint but don’t have internet access, you can simply
extract the content of this file and simply run the ‘install.sh’ file
(just double click on it and choose ‘Run in Terminal’) to install the
codecs. I would like to take this opportunity to give my thanks to Linux
Mint developers on their broader understanding of their user base. I’m
more than sure that thousands of people all around the world will
appreciate it. Not everyone is so fortunate to have high speed internet
connections to their computers, but sadly some core GNU/Linux developers
don’t exactly see things in this light. Their ‘vision’ is very narrow.
I installed VLC manually for my multimedia needs and so far I’ve
never come across any issues while playing videos (both on my Intel and
Nvidia GPU). I use Google Chrome as my web browser nowadays (Chrome
isn’t included by default) and Chrome comes with the latest version of
Adobe Flash. I’ve been watching many Flash videos online for the past
few days on Linux Mint on Google Chrome and haven’t come across any
issues. It too has been quite satisfying.

I’m not a heavy Skype user, but I’ve been using the official but
outdated Skype on Linux Mint 18 Cinnamon and except for that floating
tool bar thing (again, I’m no avid Skyper, don’t know what’s that thing
called), Skype too has been flawless. From system tray icon to
audio/video (incoming and outgoing video feed from the webcam) calls,
everything worked extremely well. About the floating tool-bar, I can’t
move it around or use any of its functions either (nothing happens when I
click on its various buttons -- close, stop the call etc).

I also had to install Teamviewer to troubleshoot a Windows 8.1 laptop
that belongs to one of my aunts and it too worked without any issues
whatsoever. So all in all, Linux Mint 18 has been able to easily satisfy
my everyday needs as an end-user.
Performance Comparison
Now allow me to share with you the performance related data. First I’ll start off with the Boot-up Speed.
Boot-Up Speed
Boot-Up speed means from the moment I hit enter at the GRUB boot-menu
till the desktop gets fully loaded. Although since I always keep the
Wi-Fi turned on connected to my Wi-Fi router, I don’t necessarily wait
till the Wi-Fi connection is ready, if the rest of the startup apps
of the desktop are loaded. If the rest of the desktop is fully loaded,
then I simply stop measuring (I use the timer app on my Android phone
for measuring the time) despite the current state of the Wi-Fi
connection.

As you can see both Ubuntu 16.04 LTS and Linux Mint 18 Cinnamon
scored quite similar speeds while booting, although, Linux Mint 18 was
about
4.4% faster (1.5 seconds). This could be ‘explained’ when you look at the memory usage readings.
Memory Usage Upon Desktop loading
Unlike with Boot-up Speed measurement, I wait till all the aspects of
the desktop is fully loaded (Wi-Fi connected, all the startup apps
fully loaded, startup notifications finished etc) before I measure the
memory usage. I also had previously added the system monitor shortcut to
the task-bar because if I was to open it by navigating or searching
through the start-menu that would’ve increased the memory usage reading
thus negatively affecting the reading. Once I open the System Monitor, I
also waited about 10-20 seconds to let things settle down as well. Only
after that I noted the current memory usage reading and wrote it down
(this is how I’ve been doing it in all these years actually).

As you can see, Linux Mint 18 Cinnamon consumed
32.3% less memory compared to Ubuntu 16.04 LTS. In other words, while booting, Linux Mint 18 had
32.3% (about
205 MiB) less data to be
copied over to RAM
from the main storage (because that’s what happens when an operating
system boots) and that may explain why Mint was slightly faster to boot.
CPU Usage at Idle

On both operating systems, the CPU usage at idle (meaning no actively
running user applications -- web browsers, text editors, music managers
etc) was extremely low (about
1% at most). And on many occasions it even reached
0% as well. Impressive!
Power Usage at Idle
For measuring power I use a tool called ‘
powerstat‘.
I close all the other user applications before running this
command-line tool and leave the computer alone. I also make sure to have
set the screen brightness to its maximum level, disable the screen
turning OFF and Screensaver from running. Bluetooth is also OFF and
Wi-Fi is turned ON, connected to the router. The video device (GPU) used
while measuring the power was the Intel GPU. If I had used Nvidia 920M
the readings would’ve easily been much higher.
Here’s are two screenshots from Ubuntu 16.04 LTS and Linux Mint 18 Cinnamon:


Here’s the graph I created based on the gathered data:

They’re pretty much identical, although Linux Mint 18 did do slightly better. According to my notes,
I was able to use the laptop for about 4.5 hours
with screen brightness set to 15%-25% (I only use it indoors) and using
the Intel GPU for primarily using for browsing web (including for
writing a portion of this Linux Mint 18 Cinnamon review), also took a
Skype call for 1 hour and 30 minutes (only used the webcams from both
ends for about 40 minutes), ran Teamviewer once, and used VLC to watch
some local videos on the HDD (when doing that I had turned OFF Wi-Fi).
I also installed a power usage reducer (optimizer) called TLP (
sudo apt-get install tlp) and as you can see from the below screenshot, it was actually
able to reduce the power usage of Linux Mint 18 by around 21.5% which is a lot!, as far as power usage is concerned.

Hardware Recognition
As I said in the beginning, this is a brand new laptop and unlike my
previous one which I hand picked, had almost all of its hardware
being ‘linux friendly’. This one however has one or two that could give
me some trouble. Those will be the FocalTech touch pad, Qualcomm Wi-Fi
adapter and the Nvidia 920M GPU (or the whole hybrid GPU setup).

But luckily, all of these hardware were recognized by Linux Mint 18. I
always like to use the proprietary GPU driver for the Nvidia 920M GPU.
Installing it was so easy because Linux Mint ships with the driver
manager that Ubuntu comes with.
Another added advantage of Linux Mint 18 was that it comes
pre-installed with an applet that once you’ve installed the proprietary
GPU driver for the Nvidia or AMD/ATI (Intel GPUs release open-source
drivers which are included by default with the Kernel so no need to
install them manually), you can switch between the two by clicking on
the applet that’s running on the system tray area, although that still
requires you to log out from the system. It also shows the currently
active GPU as well.

Wi-Fi and Blutooth adapters were all properly configured and Linux
Mint 18 was able to correctly restore the previously set status (ON/OFF)
when loading the desktop. The FocalTech touch-pad seems to have had
some issues with the Kernel in the near past, but it worked well by
default on both operating systems. However, when the laptop recovers
from Sleep (suspend), the touch-pad refuses to work. I tried many of the
tips available online (removing the kernel module and re-inserting it)
but none of it has worked so far. The only way to recover from it is to
reboot the laptop.
So far, I’ve also never seen any core system utility or any user
application crashes on both these operating systems either. So other
than the touch-pad related issue, all the rest of the hardware (display
screen, audio etc) and software has worked excellently on both operating
systems.
System Responsiveness
It’s the main storage device of your computer that acts as the
bottleneck when it comes to performance because it is one of the most
important components of your computer (because it holds all of your
data), but it is also one of the most slowest. Therefore, if an
operating systems fails to intelligently manage the main storage device
(especially when it is busy -- too many read/write requests), then that
can lead to many performance related issues. This is also why operating
systems tend to be horribly unresponsiveness when the main storage
device is under stress. Therefore, one of the best ways of measuring the
quality of an operating system is to actually make the main storage
device quite busy and then to observe the type of responsiveness it
delivers.
So what I usually do is very simple. I copy a file that’s about
1.5-1.6 GB within two locations of the logged in user’s Home folder. And
just after as I’ve initiated the file copy process, I try to play a
multimedia file (here I used VLC that I manually installed), and then
try to open up a few programs through the start-menu by searching (this
adds more ‘pressure’ on the hard disk because when you search for
something it increases hard disk read requests). And then I also try to
open a folder filled with a reasonable amount of files thorough the file
manager, again to put as much ‘pressure’ on the main storage device as
possible. While all this is happening, I also observe the mouse
pointer’s behavior. For what? The answer is simple. Have you observed
that when your computer becomes slow due to a busy hard disk, under
sever conditions, the mouse pointer has a tendency to lose its
responsiveness (its movements loses the smooth fluid nature that it
previously had)? Thus, it’s also another pointer of the responsiveness
of the operating system that you are testing.
So my judgment is as follows. Before the file copying finished, if
the operating system was able to open most of the programs I tried to
open, if the multimedia playback was able to keep on going without too
many major interruptions and all the while, if the mouse sensitivity was
not severely lost (because we’re talking about really stressing the
storage device thus some lost is assumed), then I consider the operating
system to be a responsive one. So I carried out the same test under
both operating systems, and what was the end result?
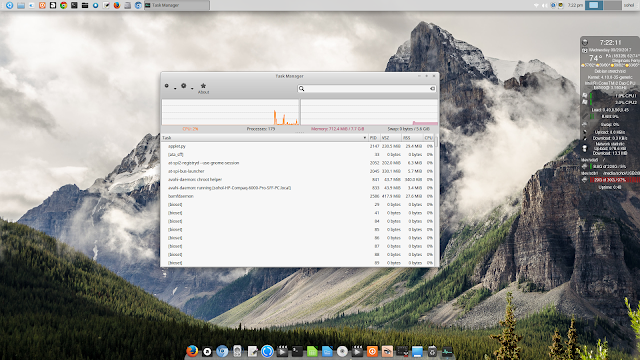
Below image is just an illustration, no need to get too excited !

It was really good under Ubuntu 16.04 LTS, but under Linux Mint 18 it was even better,
it was superb!
This is not surprising, because Linux Mint has always been an amazingly
responsive under heavy disk stress. Both operating systems were able to
open most of the programs I tried to open, play the multimedia file
without any interruptions actually, didn’t lose the mouse pointer
sensitivity at all, although file manager took a couple of seconds to
open the location
which is totally fine by me. So all in all,
I was extremely pleased with Linux Mint 18 Cinnamon’s responsiveness.
Shutdown Delay

As you can see, Ubuntu 16.04 LTS is the clear winner here where it lead Linux Mint 18 Cinnamon by being
76% more faster. However, I don’t put a whole lot of empathize on the shutdown delay unless the delay is quite long, but
6.7 seconds of shutdown time is more than tolerable.
Final Words
Even after all these years, Linux Mint 18 Cinnamon is still lean on
memory usage, boots relatively fast (compared to many other
distributions), power efficient, extremely responsive, ran on the
hardware very well (except for the touch-pad related issue which is not
exactly Linux Mint’s fault), very stable and shutdown time was also
quite good. As mentioned, the desktop is very easy to use, gives you a
lot of options to customize, yet retains a sense of simplicity. And
other major concerns of an everyday user nowadays such as Skype, web
browsing, Adobe Flash playback, Teamviewer, multimedia playback etc were
all extremely satisfying from my end.
I’ve witnessed a lot of respect for this GNU/Linux distribution over
on many occasions, and this release is no exception. My verdict is
simple: “
This is how it should be done!” Thank you for reading (if you’ve made it this far) and please go to
this page for the download instructions and to read the release notes (make sure to read it). Good luck.
Source: https://www.hecticgeek.com/2016/07/linux-mint-18-review/